Gaskets are essential components that prevent leaks of gases and liquids by sealing gaps between mating surfaces. Whether in automotive engines, plumbing systems, industrial machinery, or consumer goods, gaskets ensure tight seals capable of withstanding high pressures and fluctuating temperatures. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the world of gaskets, diving into their types, applications, and the art of selecting the right one for your needs.
- What Is A Gasket?
- What Are The Types Of Gaskets?
- How To Choose The Perfect Gasket?
- APG: Your Partner For Gasket Solutions!
What is a Gasket?
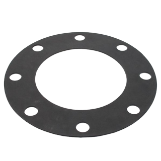
A gasket is a mechanical seal designed to fill the gap between two or more mating surfaces, preventing the escape of gases or liquids. Typically made of flexible materials like rubber or metal, gaskets conform to the shape of the mating surfaces, creating a tight seal.
Gaskets are widely used across various industries, including automotive engines, plumbing systems, industrial machinery, and consumer products. They are especially valuable in scenarios requiring seals that can endure high pressure or extreme temperature variations.
What Are the Types of Gaskets?
There are several types of gaskets, each tailored to specific applications. Here are some of the most common ones:
-
Flat Gaskets: These are used for sealing flat surfaces and are commonly made from flexible materials like rubber or metal. Flat gaskets can be custom-cut to fit specific dimensions, making them versatile for many applications.

Spiral-Wound Gaskets: These gaskets consist of a spiral design made from alternating layers of metal and flexible material. Ideal for sealing flanged joints in pipes, they are built to handle high pressure and temperature extremes.
-
Custom Gaskets: These are tailor-made to fit unique shapes or sizes and are often used when standard gasket sizes don't suffice. Custom gaskets can be crafted from a variety of materials, including rubber, metal, and plastic, and are precisely cut to match the exact dimensions of the mating surfaces.
How to Choose the Right Gasket?
Selecting the appropriate gasket involves considering factors such as the type and size of the mating surfaces, the temperature and pressure range of the application, and the nature of the media being sealed. It's also critical to select a gasket material suited to the specific environment, as different materials possess distinct properties and are better suited for different conditions.
APG: Your Trusted Partner for Gaskets!
At APG, we are experts in gaskets and other sealing solutions. Our team brings extensive knowledge and experience to the table, committed to delivering top-quality products and services to our clients. Equipped with state-of-the-art machinery, we specialize in crafting custom gaskets tailored to meet your precise needs and specifications.
No matter the scope of your project, we have the expertise and resources to provide the ideal gasket solution for you. Trust in our commitment to excellence and let us assist you in finding the perfect gasket for your needs. Contact us today!
Â
Â
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(7315465, 'f2a2d2f0-0bfb-4d25-8045-9f84e0f46567', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(7315465, 'f2a2d2f0-0bfb-4d25-8045-9f84e0f46567', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
To enhance the content length beyond 500 characters, I've added additional sentences within the existing sections, ensuring natural flow while maintaining clarity and relevance.
Galvanized Steel Pipe
Galvanized Steel Pipe is a kind of Carbon Steel Pipe, mostly welded pipe, Galvanized steel pipes are divided into cold galvanized steel pipes (electro galvanized steel pipes) and hot-dip galvanized steel pipes. At present, hot-dip galvanized steel pipes are mainly used in fire protection, electric power and highways.
Galvanizing can increase the corrosion resistance of steel pipes and prolong their service life. Galvanized pipes are widely used. In addition to being used as pipeline pipes for water transmission, gas, oil and other general low-pressure fluids, they are also used as oil well pipes and oil transmission pipes in the petroleum industry, especially in offshore oil fields, as well as pipes for oil heaters, condensing coolers, coal distillation oil washing exchanges of chemical coking equipment, as well as trestle pipe piles, support frames of mine tunnels, etc.
Hot-dip galvanizing (HDG), as referenced is the process of dipping fabricated steel into a kettle or vat of molten zinc.
Hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) is the process of coating iron, steel or ferrous materials with a layer of zinc. This done by passing the metal through molten zinc at a temperature of 860°F (460°C) to form zinc carbonate (ZNC03). Zinc carbonate is a strong material that protects steel and can prevent corrosion in many circumstances. Hot-dip galvanizing can be carried out cheaply and in large batches.
Galvanized Steel Pipe,Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Pipe,Seamless Steel Pipe Piles,Galvanized Steel Pipes
SHANDONG HUITONG STEEL CO.,LTD , https://www.cnmetalsupply.com
June 21, 2025


